Introduction
SOL to ETH refers to exchanging the Solana token (SOL) for Ethereum's native token (ETH). Simply put, you are moving value from the Solana ecosystem to the Ethereum ecosystem in a way you can use ETH, trade it, or keep it on Ethereum-compatible platforms.
What does “SOL to ETH” actually mean?
If you say “SOL to ETH” you are describing one of two things — trading SOL for ETH on a single platform, or moving value from the Solana to the Ethereum blockchain in a way that an Ethereum-native version of SOL or native ETH ends up on the other chain.
Swapping takes place most often on a central exchange or an aggregator where the exchange facilitates the conversion for you. Bridging encompasses locks, wrapped tokens, and cross-chain messages so assets can exist or be utilized on another chain while still remaining attached to the initial tokens.
Each route carries different fees, velocity, and security compromises. Centralized exchanges are simpler and safer for most, but bridges offer more direct DeFi exposure with protocol risk.
Key Terms and Concepts
- SOL — the native token of the Solana blockchain, for fees, staking, and use in the ecosystem. Interested in staking SOL? See our Solana (SOL) Staking Guide.
- ETH — Ethereum's own token, for paying gas, unlocking the functionality of a smart contract, and engaging in Ethereum DeFi and NFT markets.
- Bridge — a cross-chain protocol for moving assets or message proofs from one blockchain to another, most commonly done through locking or burning the original asset and minting a corresponding wrapped version on the receiving chain. Examples include Wormhole, Allbridge, and Synapse.
- Wrapped token — a token on chain B representing an asset locked on chain A (e.g. wrapped SOL on Ethereum). It can only be redeemed for the original asset via the bridge mechanism.
For insight on staking other tokens, check out our XRP Staking Guide.
A Very Short History — Why They Exist

Ethereum made its mainnet release in July 2015 and became the de facto platform for DeFi and smart contracts. Solana published its mainnet beta in early 2020 with stronger performance and lower fees to serve performance-focused apps. Those different strengths amassed demand for cross-chain value transfers.
As DeFi grew, customized cross-chain bridges were developed to facilitate token transfers without exchange sales. Wormhole, Allbridge, Synapse and more gained popularity for transfers between Solana and Ethereum. However, bridge hacking and contract risk shaped user prudence and industry responses.
For a complete guide on token swapping, see USDT to BTC: A Complete Guide.
Two Popular Methods of Swapping from SOL to ETH
Centralized exchange — deposit SOL on a platform like Binance or Coinbase, exchange SOL for ETH, then move ETH to your Ethereum wallet. It's the simplest solution. Exchanges offer converters with real-time pricing and are easy to use.
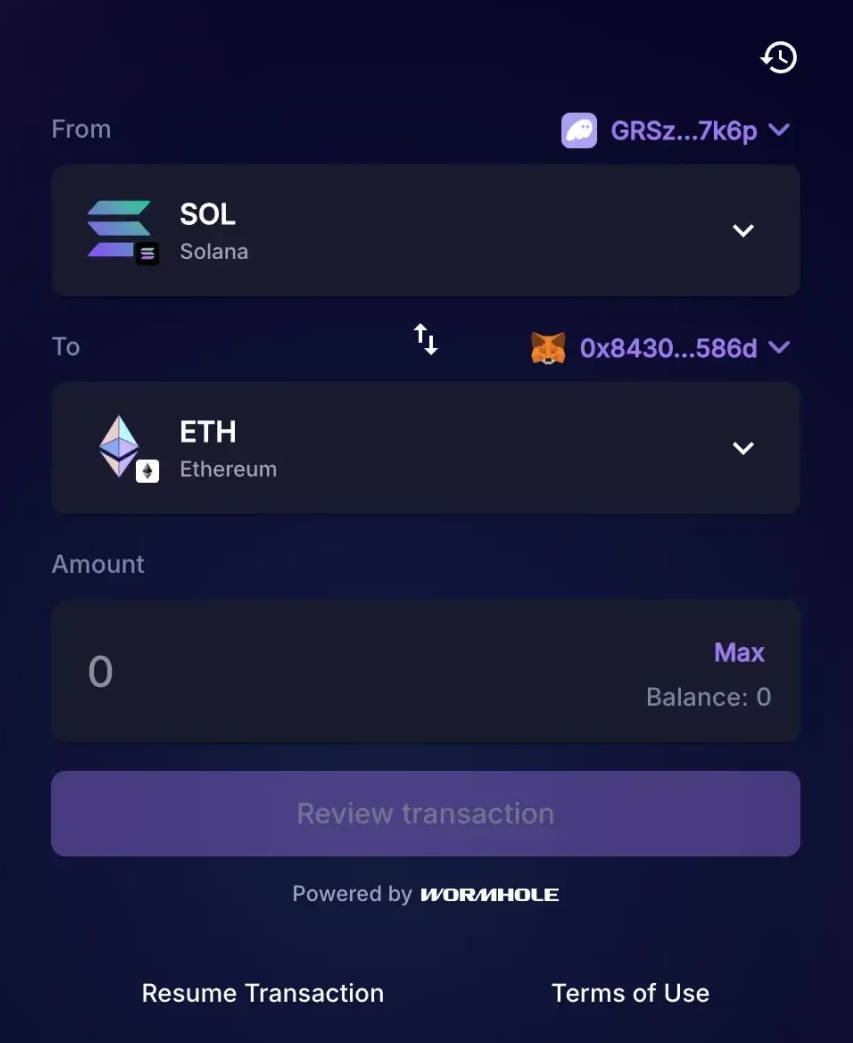
Swap interface example showing SOL to ETH conversion flow, reminiscent of centralized or aggregator platforms.
Bridge + exchange — use a token bridge to move SOL to Ethereum as a wrapped token or move a stablecoin from one chain to another and then exchange the wrapped token for ETH on an Ethereum DEX. It leaves you in control of your keys but needs more steps and protocol risk.
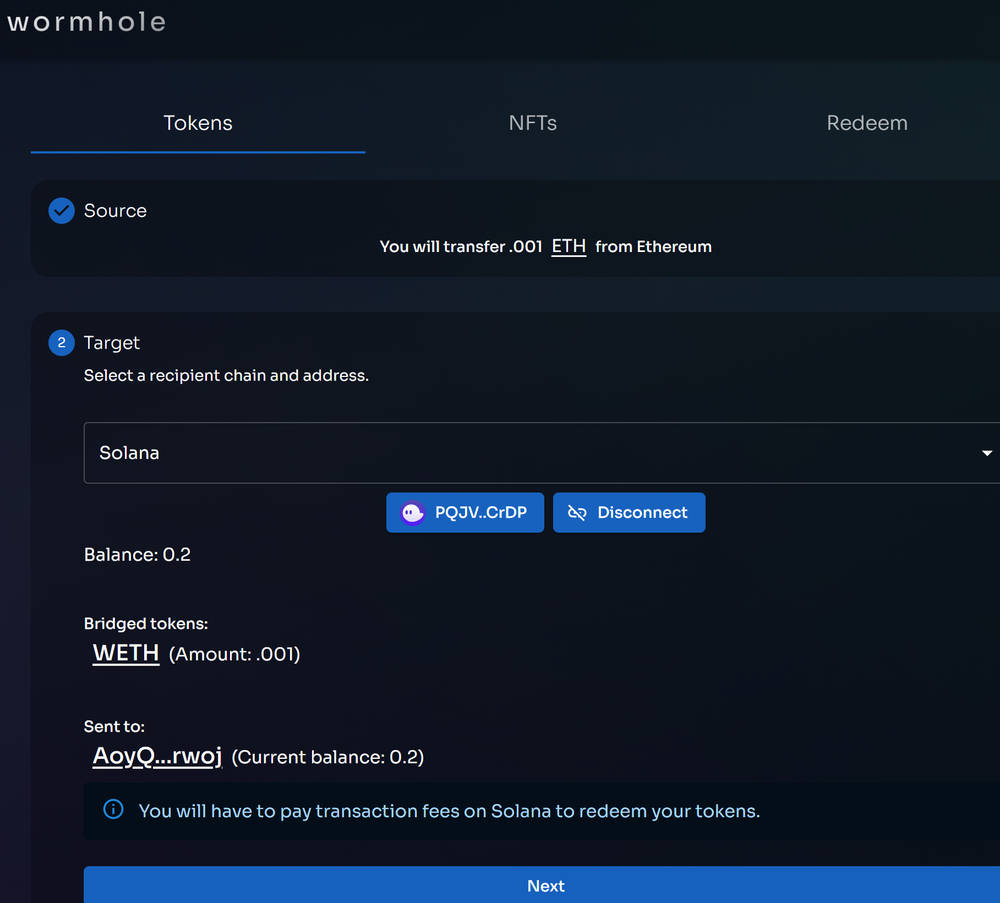
Wormhole bridge interface showing source (Solana) and target (Ethereum) selection, and wrapped token initiation.
How Token Bridges Function — The Low-down
Most of the bridges function in the following manner: you lock tokens into the bridge on Solana; the bridge examines the action and initiates a mint or unlock on Ethereum; you receive a pegged or wrapped token on Ethereum, a representation of your original SOL.
It relies on having cross-chain messages ratified through validator sets, relayers, or contract proofs. These each introduce potential centralization or technical danger.
Always review the bridge's paperwork, security audits, and reputation in the community before depositing funds. Reliable bridges release technical docs and occasional insurance or backstop agreements.
Visual representation of cross-chain transfers — “Transfer stablecoins between EVM & non-EVM chains” — as seen in Allbridge’s informational banner.
Popular Tools and Bridges You Can Use
- Wormhole — a bridge from Solana to Ethereum and other chains. It provides token transfers as well as message passing.
- Allbridge — a cross-chain bridge for transfers from/into Solana and Ethereum with controlled flows and swap functionality.
- Synapse — a cross-chain router and liquidity network for supporting Solana routes and competitive fees.
- Centralized exchanges — Binance, Coinbase and others let you swap SOL for ETH in a couple of clicks and with little technical risk.
Step-by-Step Example — Bridging through Wormhole
- Connect a Solana wallet (e.g. Phantom) and an Ethereum wallet (e.g. MetaMask) to the Wormhole bridge UI.
- Approve the transfer of SOL on Solana — the bridge deploys or burns the SOL on Solana and releases a message signed by Wormhole validators.
- Gather your wrapped SOL or desired token on Ethereum by submitting the proof and paying gas. You can then trade your wrapped token for ETH on an Ethereum DEX or centralized facility.
Each step requires payment for native chain fees (Solana transaction fee — low most of the time, Ethereum gas — high).
Phantom wallet interface supporting both Solana and Ethereum ecosystems.
Real-World Case Study — Wormhole Exploit and Lesson
Wormhole was exploited in February 2022, for a loss of nearly $320 million in wrapped tokens. It highlighted the magnitude of loss a hole in a bridge could cause and why backstops, audits, and rapid responses are necessary.
Lesson — bridges are durable but carry concentrated protocol risk. That's why some people switch through exchanges or split funds across tools.
Costs, Speed and Practical Notes
- Centralized exchanges — fees are set according to trading and withdrawal fees, and you hand over custody to the exchange for the duration of execution.
- Bridges — Solana-side steps are fast and cheap; Ethereum-side claiming and swaps are slow and pricey with gas. Plan for bridge fees and possible slippage when swapping wrapped tokens for ETH.
Practical guidance: check wallet addresses, use the correct bridge websites, make small transfers before large ones, and keep transaction IDs.
Objective Analysis and Conclusion
If you value custody and want direct interaction with DeFi on both networks, using a bridge alongside swaps is practical but involves technical and security risk. If you want simplicity and low protocol exposure, using a regulated centralized exchange is the smarter option for most.
Both are acceptable depending on objectives, technical comfort, and risk tolerance. Use reputable, well-documented tools and keep amounts balanced until you feel comfortable.
FAQ
Q: Can you transfer SOL directly to your Ethereum wallet?
No. Ethereum and Solana use different blockchain and address formats. You must use a bridge that releases a wrapped version on Ethereum, or exchange SOL for ETH on a trading site.
Q: Are bridges safe?
A: Bridges are convenient but carry added technical risk: bugs in a smart contract, key compromise, or validator failure have in the past caused major losses. A classic example was the Wormhole exploit in 2022.
Q: Is it the cheapest method?
A: It can be cheaper on the Solana end but might have steep Ethereum gas when claiming. Centralized exchanges may offer lower spreads but can include withdrawal fees.
Q: How long does a bridge transfer take?
A: Times are protocol- and congestion-dependent. Solana transfers are generally near-instant; finality and claiming on Ethereum depend on confirmations and gas price.
Q: Can you trade wrapped SOL for Ethereum's ETH?
A: Yes. You can trade on Ethereum DEXs for ETH after wrapping SOL on Ethereum, but pay attention to liquidity and slippage. Or you can use a centralized exchange to bypass on-chain steps.


