What Is DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) in Crypto?


Although blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are the notions often used interchangeably, blockchain is only one instance of DLTs. Instead of working out such disadvantages of blockchain as high fees and excessive energy consumption, some developers chose to create new DLTs without these drawbacks from scratch.
Notable examples of distributed ledgers include Hashgraph, Holochain, and Tempo. This article describes a technology known as Directed Acyclic Graph, or DAG. Here you can learn how DAG works, what are the benefits of this technology, how it is different from blockchain, and what projects use DAG.
Contents
What Is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)?
A directed acyclic graph, or simply DAG, is a tool for data structuring and modeling often used to organize transaction data in cryptocurrency networks and maintain consensus.
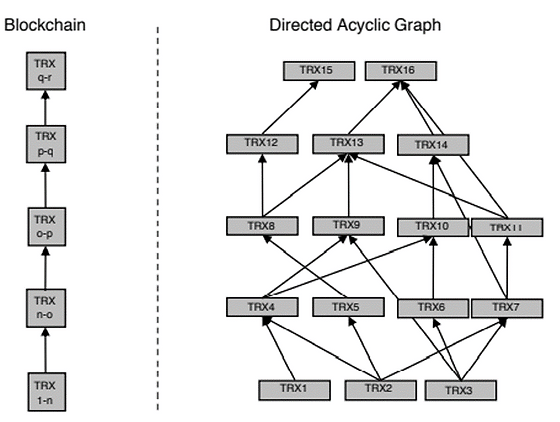
Image source: Mo Ashouri
In contrast to blockchain, in DAG-based networks transactions are not organized in blocks. Instead they are built of vertices and edges. Every new transaction is added as a vertex on top of a previous vertex. A new transaction can't be added if it doesn't reference the previous transaction. Transactions are submitted by the nodes performing tasks in order to protect the network from spam attacks, in other words, directed acyclic graph relies on proof-of-work.
How Does DAG Work?
A directed acyclic graph has a tree-like structure. The nodes submitting transactions serve as branches of that tree. This structure helps to store data more efficiently if compared to blockchain. It is possible because in DAG-based networks nodes can have different parent roots which allows to validate several transactions simultaneously. Instead of waiting in line, different transactions are processed at the same time and quickly get added to the ledger.
To achieve coherence and integrity, every new transaction references the previous one and cannot be added to the network without this reference. One vertex stands for one transaction. A newer transaction is stringed upon the previous one. Blocks and block mining are not used in DAGs. However, the nodes must perform tasks that protect the network from spam transactions and harm.
To prevent double spending nodes check the strings of transactions to verify if the latest transaction leads to the first one. If everything works fine, then the sender's balance is sufficient. If the string of transactions turns out to have mistakes, the latest transaction will not be added. Some networks use an algorithm that picks the best branches for new transactions. If a new transaction is fit for several different paths at time, the algorithm chooses the one with more confirmations leading to a vertex.
DAG Technology Key Benefits
The benefits of the DAG model are as follows:
High speed: DAG-based cryptocurrencies boast fast transactions
Low fees: Some of the DAG-based cryptocurrencies don't collect fees at all, while others charge small commissions
Eco-friendly: DAG doesn't rely on mining, so it doesn't impact environment in a fashion that Bitcoin does
Additionally, it’s safe to say that DAG has a potential for maintaining a high level of decentralization. However, it depends on the success of the DAG-based platforms in drawing large numbers of users. A high level of decentralization means better security.
DAG vs Blockchain
As the name suggests, blockchain is organized as a chain. The DAG's name is pretty self-explanatory too, as a directed acyclic graph is organized as a graph. It is implemented in crypto as it allows to solve some of the blockchain's inherent problems, like scalability issues, etc.
More than that, DAG is capable of maintaining a wider decentralization than blockchain. Also, it eliminates competition for the block from the mining formula. More than that, the mining itself (like the one used by Bitcoin) is not used in the DAG-based systems. It brings two huge advantages over blockchain. First off, the DAG systems are more eco-friendly. They don’t consume as much energy as proof-of-work-based blockchains. The second advantage is the lack of network fees which makes using the DAG-based networks cheaper for users to a large benefit.
In the blockchain-based networks, new transactions can't be validated until the block of previous transactions is mined. It creates inherent speed limitations to these networks. DAG’s formula allows for faster operation as it doesn’t use blocks and the nodes validate multiple separate transactions simultaneously, adding them on top of the best-fit vertices.
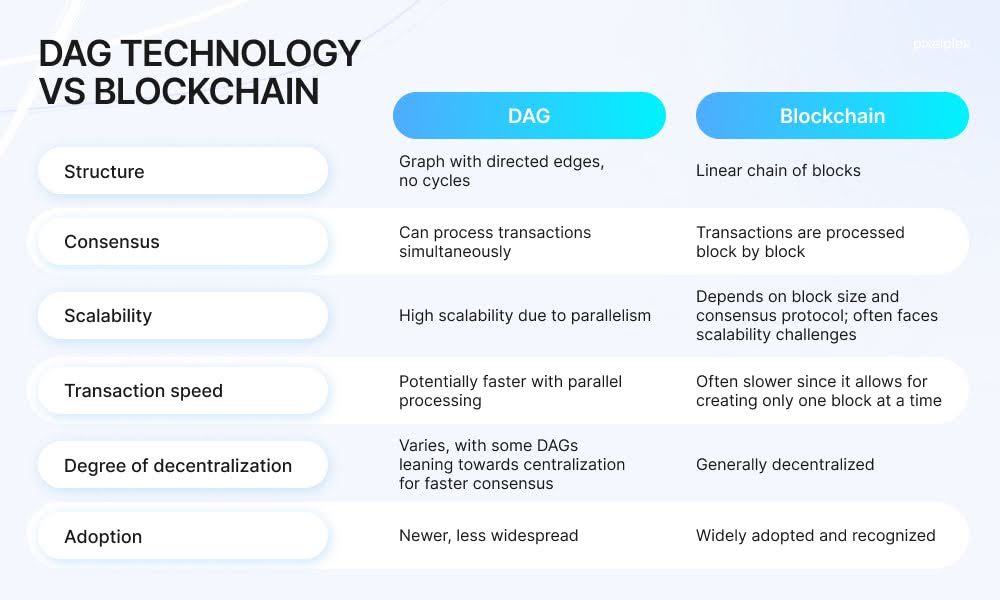
Image source: PixelPlex
Despite the obvious advantages of a directed acyclic graph over blockchain, it lacks a crucial component of the latter -- decentralization. This drawback is not inherent for DAG though. This model has a potential for strong decentralization. Rather the reason for this is that the directed acyclic graph is a pretty young technology, not as established as blockchain. DAG-based networks cannot boast amounts of active nodes similar to the likes of Bitcoin or Ethereum. It hinders the decentralization growth of the DAG-based networks from the start.
What Projects and Protocols Use DAG?
As of 2024, the DAG implementation in cryptocurrencies is at its early stages. However, several of the crypto projects using DAG have achieved recognition. At the time of writing, IOTA is among the top 100 cryptocurrencies by market cap, while Obyte and Nano enjoy some more moderate success. And this is not the full list of cryptocurrencies using a DAG framework.
IOTA
IOTA (Internet of Things Applications) is an open-source web3-ready platform based on the DAG called the Tangle. IOTA was launched in 2017. It can be used to run smart contracts, financial operations, build and host dApps, mint NFTs and native tokens, work with custom EVM chains, and more.
IOTA has a unique approach to validation. To make a transaction, the user must validate two others. It saves energy while increasing decentralization. More than that, the IOTA structure allows for cost-effective transactions.
Nano
Nano is a lightweight crypto characterized by lightning-speed zero-fee transactions, making it a natural choice as a means of payments. The project started to develop in 2014 and was branded as Nano in 2018. The network combines the blockchain technology and DAG.
Nano relies on an innovative consensus mechanism known as Open Representative Voting (ORV) that requires a limited number of chosen validators who do the job of validating transactions on behalf of their voters. This approach saves energy and extremely increases the transaction speed.
Obyte
Obyte is among the earliest cryptocurrencies based on the DAG model. It was launched back in 2016. The project was built with the aim of creating a truly equal and decentralized network that doesn't require mining farms and any kind of intermediaries. The transactions on Obyte are untraceable.
The Obyte ecosystem is used to build safe dApps on top of it. The network is connected with Ethereum via the Counterstake bridge. As Obyte uses a double check for transaction validation, it charges transaction fees.
Future Prospects
The DAG model is still a relatively young technology and it certainly has room to grow. On the one hand, it addresses most issues associated with blockchain technology. On the other hand, as the framework is not tested as good as blockchain, its capabilities and possible drawbacks remain unexamined. The growth of implementation of the DAG model will show its true value and potential. It's early to declare that the directed acyclic graph can replace blockchain.
FAQs
What is DAG used for?
The DAG model is used for processing and organizing transactions in the cryptocurrency networks. Its structure allows validation of multiple transactions at the same time which makes the validation process faster and cheaper than in the blockchain-based networks.
Are DAGs superior to blockchains?
Although a directed acyclic graph has undisputable advantages over blockchains, the latter are still prevalent. The reason lies in the fact that DAGs are yet to be well-explored and we don't know much about their potential limitations. Many developers prefer to try to work out infamous issues of blockchain rather than to put their feet on the little-known grounds of technologies like DAG.
Is DAG connected?
The DAG system is connected, however, the connection between its parts is quite weak. The strong connection could have existed if DAG used a single vertex which is usually not the case.

Los mejores tutoriales
-
Что такое хард-форк?Jul 27, 2020
-
Стейкинг на Ethereum 2.0 и его основные особенностиAug 01, 2020
-
Инновации на основе блокчейна в сфере энергетикиAug 03, 2020






No hay comentarios aún. ¡Sé el primero!