Liquid Staking: Meaning & Examples


The proof-of-work based blockchains like Bitcoin draw significant criticism due to excessive energy consumption and vicious environmental impact. Many consensus mechanism options emerged in the 2010s, and proof-of-stake became one of the most popular. Staking is the mechanism used for transaction validation and governance through locking portions of funds for months, which in turn brings incentive rewards to those who stake.
Nowadays, there are several forms of staking out there so that token owners can use different approaches to make money though staking. As the staked tokens are locked, investors cannot trade or use them for yield farming until the end of the staking period. Liquid staking addresses this issue via giving investors who stake tokens some other tokens in return so they can use these tokens for yield farming or trade them.
This article provides a full guide on liquid staking which includes the definition of staking in general, liquid staking, and the differences between the two. Also it answers what are the risks and benefits of liquid staking, what are examples (including some liquid staking protocols and tokens), and what is the difference between centralized and decentralized liquid staking?
Contents
What Is Staking?
Staking is the act of locking up cryptocurrency as collateral to participate in the network governance, validate transactions, and so on, depending on the particular rules of the blockchain or a smart contract corresponding with this cryptocurrency. Staking is used for maintaining many blockchain-based ecosystems (like Ethereum or EOS) and for some standalone DeFi applications.
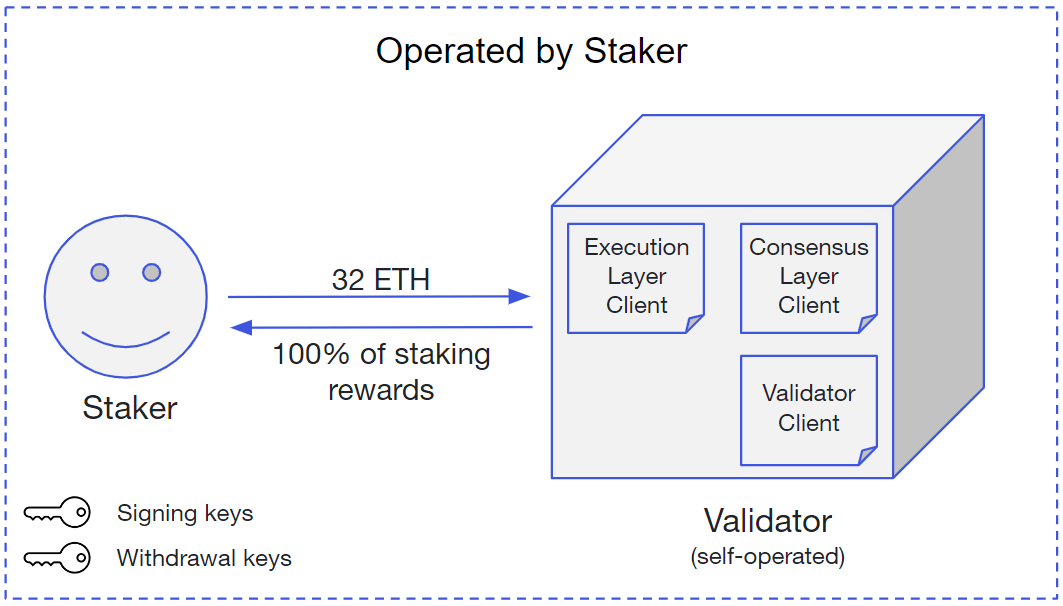
Image source: Consensys
Rewards and penalties are the important element of staking. The proof-of-stake-based networks incentivize users to validate fair transactions and enhance security in general via staking rewards. If the node attempts to violate the network rules and jeopardize the security it results in penalties, meaning that the stake (collateral) is taken away.
Some people run staking nodes solo while there are many options of using staking as a service (SaaS) services. What sets people back from regular staking is the need to lock tokens up. It draws risks as investors can miss out on other good opportunities or simply won't be able to use their money in an emergency.
What Is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking is the staking type that addresses the problem of having the funds locked up. Unlike the regular staking, liquid staking allows investors to use collateral for operations on the DeFi platforms. Liquid staking services work the following way: they stake the users' money on their behalf while giving them the freshly minted tokens that can be redeemed in exchange for the staked tokens. These tokens are called Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs) or Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) and have the same value as the underlying asset. Some blockchains have native liquid staking. It means that they don't offer liquid staking tokens. Instead they allow liquidity for the very tokens you stake. An example is staking ADA on the Cardano blockchain.
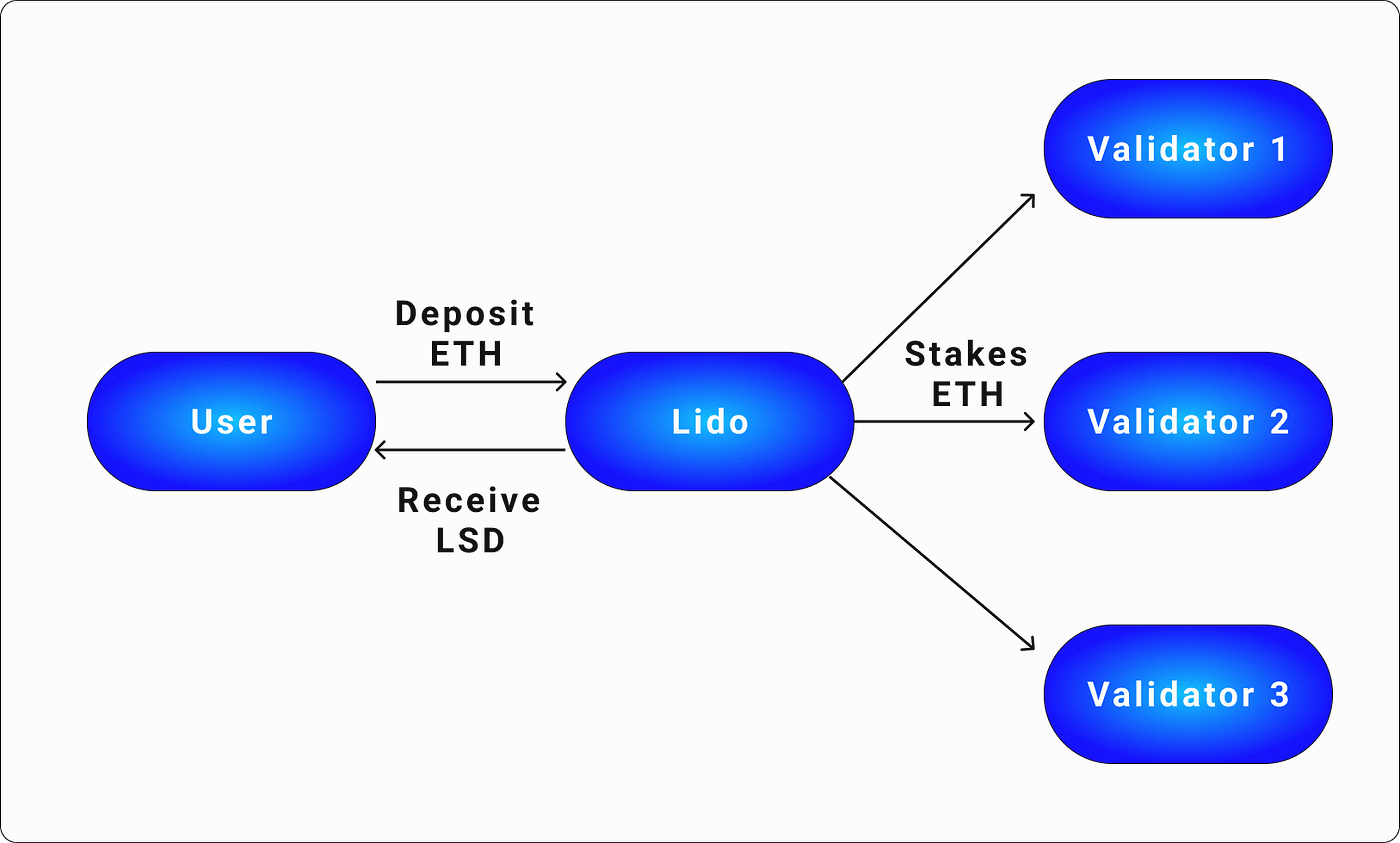
Image source: CryptoStars
These tokens can be traded or used as a collateral on the DeFi platforms. This method may seem sophisticated but in some way it allows investors to participate in staking without losing opportunities to use your funds for other purposes. In the event the investor is going to get their tokens back the unstaking process takes place. This process involves burning the liquid staking tokens via sending them to a burning address. The transaction gets verified and if everything is correct, the investor receives their tokens back. The process is pretty simple, however, it doesn't go for free. Some money will be lost in fees.
Here's how it works: let's say you stake 10 ETH via the liquid staking platform. It gives you 10stETH (staked ETH) in return. These tokens can be deposited to the other platforms where they can be used for yield farming. Considering that Ethereum requires a minimum of 32 ETH as a stake, this token is very popular on the liquid staking platforms. The most sought after LSTs are the variations of staked Ether.
Traditional Staking vs Liquid Staking
Now, let's take a deeper look at the differences between two types of staking. The main purpose of the regular (or traditional) staking is validation of transactions and keeping the blockchain safe. The demand for locking up collateral makes it harder to spam attack the network so staking is crucial for this type of blockchains. The users who staked tokens realize that violating the rules will result in losing both the stake and potential staking rewards. It's understood that the bigger the stake is the safer the platform. On the other hand, the high threshold makes staking unattractive for many investors as they don't want to lock up much money. It results in lower number of stakers hence lower level of decentralization and after all lower security.
The liquid staking operators thus increase the PoS-based networks' security through incentivizing investors to participate in staking as they don't lose the value of their funds for a lockup period. Some draw similarities between liquid staking and pooled staking however the former is different because it provides investors with assets immediately after they stake their tokens.
Benefits & Risks of Liquid Staking
Speaking of the benefits of liquid staking we can outline the following characteristics:
- Perseverance of the liquidity while staking without compromising the staking rewards
- Lower staking thresholds, meaning that investors can stake low amounts to join the staking pools
Now, let's see what are the main risks of using liquid staking:
- The risk of penalties remains as liquid stakers don't run the node themselves, hence they don't control it.
- There is a risk of security breach on the side of the liquid staking operator. In the event of a breach, the staked tokens may disappear.
- The prices of LSTs may go in an unfavorable direction incurring lower profit if any.
Liquid Staking Tokens and Protocols
The services operating liquid staking and providing investors with LSTs are called liquid staking protocols. Lido is the biggest liquid staking protocol with a multibillion TVL. The most popular LSTs on Lido are stETH, stMATIC on Polygon, and the Solana-based stSOL. Another popular liquid staking token on Lido is a Lido Staked DAO.

The second biggest liquid staking protocol is Rocket Pool. Its TVL exceeds $1 billion. As of April 2024, the Rocket Pool ETH is the third biggest LST in the market. The selling point of Rocket Pool is that it doesn't require users to stake 32 ETH. The threshold stands at the 8 ETH mark with 2.4 ETH worth of RPL needed on top of 8 ETH.
These are the examples of the biggest liquid staking protocols and tokens in terms of market cap.
Centralized vs Decentralized Liquid Staking
Lido and Rocket Pool are decentralized liquid staking protocols, meaning that they operate algorithmically and cannot be affected directly by a single entity. Moreover, they don't collect the user's personal data on servers.
However, apart from such protocols, there are centralized ones in place as well. Usually they are the parts of the bigger multifunctional platforms, for instance centralized crypto exchanges. They collect the user data and hold users' private keys while decentralized liquid staking protocols remain non-custodial.
The main risk associated with decentralized liquid staking protocols is the possibility of the smart contract fallacy. Centralized protocols, on the other hand, have risks associated with centralization. For instance, if the servers of the platform get hacked, the user funds and data can be stolen.
Conclusion
Liquid staking is a pretty lucrative format of staking as it saves the staking rewards while giving your funds to invest while the underlying assets are locked up. It makes staking less demanding and opens new horizons. As of 2024, this type of staking is already in high demand and the multibillion market cap rates mark the popularity of this technology. However, nothing comes without risks and liquid staking is not an exception. Do your own research before you decide to choose this or that liquid staking operator and estimate the risk-to-profit ratio.

I migliori tutorial
-
Что такое хард-форк?Jul 27, 2020
-
Стейкинг на Ethereum 2.0 и его основные особенностиAug 01, 2020
-
Инновации на основе блокчейна в сфере энергетикиAug 03, 2020






Qui non ci sono ancora commenti. Sarai il primo!