What Is Liquid Staking? Explained
Staking is one of the popular ways to generate passive income via cryptocurrency. However, some have reservations about this method as staking requires locking some of your money up for weeks or months. It hinders the use of this money and creates risks associated with value volatility.
Liquid staking is the solution aimed at giving stakers more flexibility and decreasing the risks through providing stakers with a kind of compensation for the tokens they lock up. This article explores the mechanism of liquid staking, shows how it is different from regular staking, outlines pros and cons of liquid staking, and answers crucial questions about the subject.
Contents
What Is Staking?
As a proof of work consensus mechanism used in the Bitcoin network requires too much energy and therefore takes a toll on the environment, developers came up with various healthier solutions. Arguably the most popular of them is proof of stake (PoS). Even such a prominent network as Ethereum switched to it from proof of work to ensure a more eco-friendly practice.
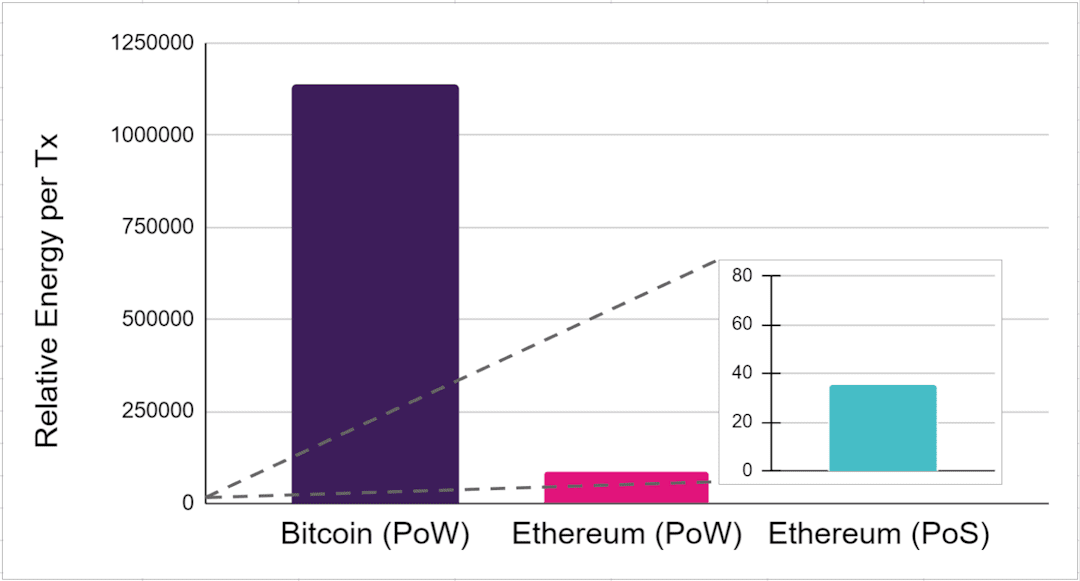
Image source: Moonbeam
To validate transactions on the network and ensure safety, proof of work based networks incorporate mining. You can't validate a transaction or changes to the network unless you perform some calculation. Spammers won’t do that.
Proof of stake replaces calculations with locking some crypto up. To incentivise people to lock their money (stakes coins/tokens), the platform pays stakers rewards corresponding with the amount staked and the lockup period. This measure also guarantees that the network's native tokens used for staking won't be dumped on the market all at once. If the validator does a bad job, violates the network's rules, and so on, the staked tokens get “slashed,” meaning that the person who staked it loses them.
Some people stake as solo operators while others prefer to use staking as service providers which offer more flexible conditions and various options that allow users to maximize profits.
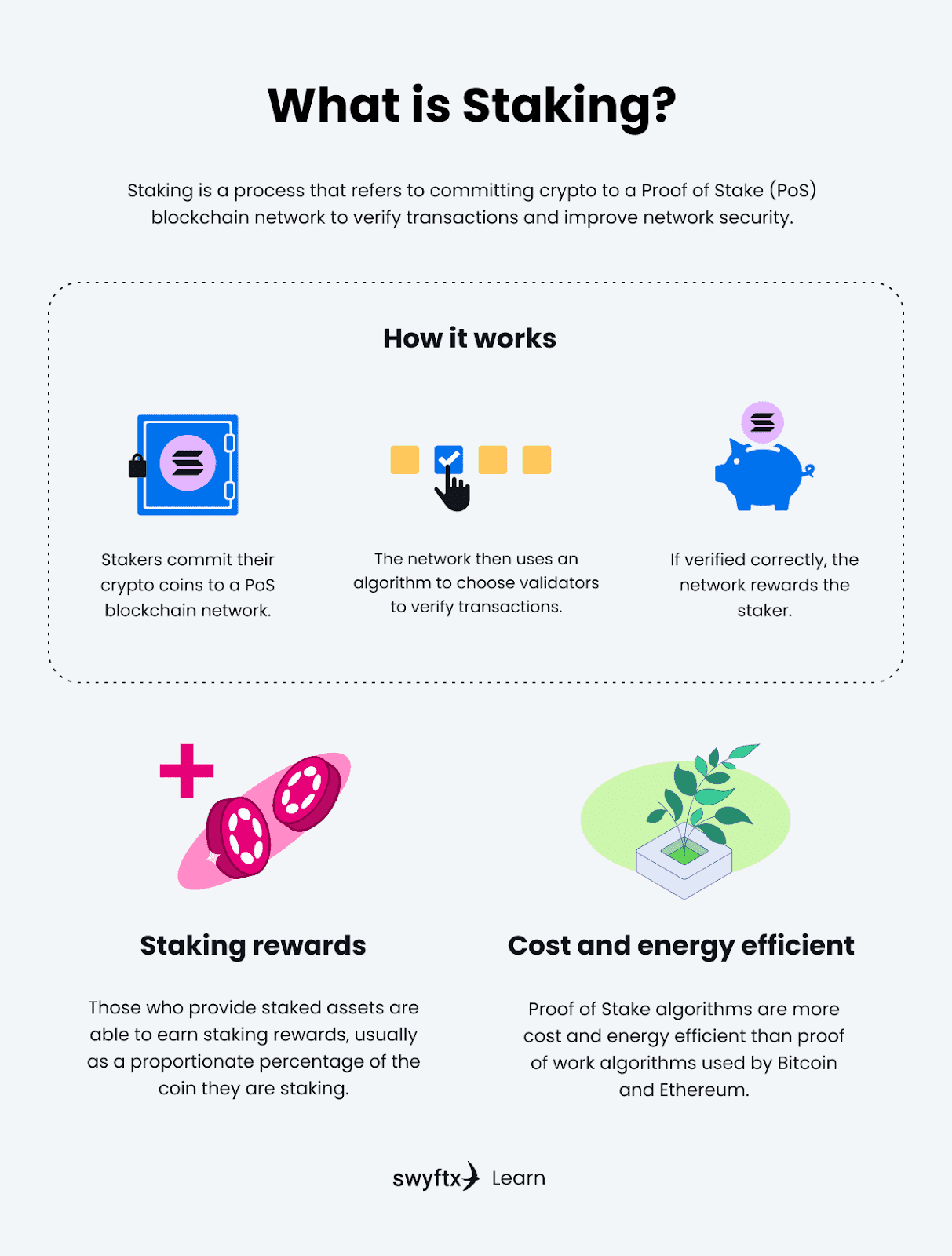
Image source: Swyftx Learn
The main problem with staking however is that during the lockup period investors cannot use their tokens. They can't spend this money, they can't use it as collateral for yield mining on the DeFi platforms. More than that, if the locked token’s price drops drastically by the end of the lockup period, an investor may end up with less value than before the staking disregard the staking rewards. More than that if you use a staking as a service platform you risk that your tokens will end up slashed for the validator's violations.
What Is Liquid Staking & How Does It Work?
Liquid staking is an attempt to solve the lockup problem (at least to some degree) and hedge against the staking risks.
It works the following way: you provide a liquid staking platform with a certain amount of some cryptocurrency to stake it on your behalf. The platform then mints the new tokens in the amount needed to represent the value of an underlying asset (the one you deposit for staking) and grants these tokens to you. For instance, if you deposit some ETH for staking, you receive a corresponding amount of stETH (staked Ether) in return. As it unlocks the liquidity for an investor, the practice is called liquid staking.
You can use these freshly minted tokens for spending, trading, or yield farming right away. Probably their value will get lower than the value of an underlying asset but still you will have an opportunity to use it for investment or other purposes instead of just having the locked up assets. It gives stakers more opportunities, more freedom of action, and makes staking more attractive in general.
Staking vs. Liquid Staking
Both types of staking have some drawbacks, however it's safe to say that liquid staking has all the risks associated with regular staking while offering some benefits on top of it.
With staking you are left with nothing until the lockup period is in effect. You can earn through it or lose money due to penalties or market volatility.
Liquid staking is the same set of risks and opportunities with extra opportunities coming from the ability to benefit from using these tokens as collateral on DeFi protocols, etc.
Pros & Cons
As any method of generating passive income, liquid staking has advantages and drawbacks.
Pros
You save the value of the funds you stake. Thanks to tokens you receive in return for your deposit your portfolio doesn't lose the value when you stake some tokens.
You have funds for yield farming. You can use new tokens on various DeFi platforms like liquidity pools, prediction markets, lending pools, and so on.
You can get more profit. While regular staking allows you to earn rewards for validation of transactions, liquid staking provides an opportunity to earn additional profit coming from yield farming.
Wider opportunities. As you outsource staking to a third party you don't have to meet all the requirements for staking. For instance, you don't have to deposit 32 ETH if you want to participate in the Ether staking (32 ETH is the minimum stake on Ethereum).
Cons
Slashing risk. Outsourcing the running of a staking node brings some risks too. If the validator using your funds is doing the job badly, your funds can end up slashed as a penalty.
Security risk. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities of the liquid staking service and steal your money.
Price fluctuations. The tokens you get in return for the tokens you deposit have no stable peg to an underlying asset. The price may change unfavourably and you should be aware of it.
Not good for governance. In most cases you cannot participate in the platform governance if you use liquid staking.
Liquid Staking Tokens and Protocols
Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) are the tokens representing the underlying asset you deposit for staking. Liquid staking protocols are the service providers.

Lido and Rocket are among the most popular protocols. Both of them are decentralized. Lido allows to receive stETH for the Ethereum tokens, stSOL for the Solana tokens, and stMATIC for the Polygon tokens. Rocket mints rETH tokens in return for deposited Ethereum tokens.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Liquid Staking
Not all the liquid staking services are decentralized. Some of them exist as a part of centralized crypto exchanges. Such exchanges are custodial, meaning they have access to the staked funds. It creates a risk of losing money in the event of the exchange server hacking or exit scam. On the other hand, decentralized services have risks of a smart contract vulnerability exploit.
Restaking and Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs)
Restaking is a mechanism of creating an additional security layer to Ethereum external systems like rollups and oracles using staked Ether tokens. Restaking tokens represent the tokens already staked via the staking services.
Conclusion
Liquid staking is an advanced way of staking. It unlocks the liquidity of the tokens you stake. You still cannot use the staked tokens but when you deposit them you receive a corresponding amount of freshly minted tokens of the same value. These tokens represent the underlying asset and can be used to redeem it. Also you can use these as collateral on DeFi platforms or trade while the original tokens are locked up.
As you outsource running the staking node, you face some risks too. First off, the smart contract of a decentralized liquid staking protocol can be hacked. If you use a centralized liquid staking service, you face security risks as well. The platform can get hacked or turn out to be a scam. More than that, the prices for tokens representing the asset you deposit for staking can decline significantly due to natural market changes.
Additionally, liquid staking protocols won't fit your demands if you want to participate in the network governance. Using a liquid staking service you usually grant your voting power to the service. If the service violates the network's rules, you lose your money in penalties. Given these pros and cons you should approach liquid staking with caution and make weighted decisions.